Schemas and Definitions
Schemas and Definitions in this module are added in a simpler way, that is, you can write it in the way you want to see the result. It is possible to add them in the definitions of the doc object seen in the Advanced Usage section, or directly to the response via the schema parameter.
Types and Examples in the schema: The type is abstracted according to the typeof of the example, and the example comes right in front of the parameter declaration. In the example below, for the user definition, the type of the parameter name will be string and its example will be John Doe, while the type of the parameter age will be number and its example will be 29.
NOTE: To configure a parameter as required, just add the symbol $ before the parameter, for example: $name = "John Doe".
Examples
const doc = {
...
definitions: {
Parents: {
father: 'Simon Doe',
mother: 'Marie Doe'
},
User: {
name: 'John Doe',
age: 29,
parents: {
$ref: '#/definitions/Parents'
},
diplomas: [
{
school: 'XYZ University',
year: 2020,
completed: true,
internship: {
hours: 290,
location: 'XYZ Company'
}
}
]
},
AddUser: {
$name: 'John Doe',
$age: 29,
about: ''
}
}
};
app.post('/users', (req, res) => {
...
/* #swagger.parameters['body'] = {
in: 'body',
description: 'Add new user.',
schema: { $ref: '#/definitions/AddUser' }
} */
...
});
app.post('/users', (req, res) => {
...
/* #swagger.parameters['body'] = {
in: 'body',
description: 'Add new user.',
schema: {
$name: 'John Doe',
$age: 29,
about: ''
}
} */
...
});
app.get('/users/:id', (req, res) => {
...
/* #swagger.responses[200] = {
description: 'Get a specific user.',
schema: { $ref: '#/definitions/User' }
} */
...
});
app.get('/path', (req, res) => {
...
/* #swagger.responses[200] = {
description: 'Get a specific user.',
schema: {
name: 'John Doe',
age: 29,
about: ''
}
} */
...
});
@definitions
By default swagger-autogen convert (renders) definitions in a simple way to Swagger specifiction. It use type inference but some users need to specify the specification on account of their needs. To bypass the swagger-autogen rendering in the definitions and put the specification Swagger directly, you can use @definitions, such as:
const doc = {
...
'@definitions': {
someParameter: {
type: 'object',
properties: {
property1: {
type: 'integer',
format: 'int32',
description: 'With no swagger-autogen render...'
}
}
}
}
};
In the case above, the definitions in the .json will be the same as in the '@definitions'.
@schema
Use the '@schema' instead of schema if you if you don't want swagger-autogen to render the schema. In this case you must build the schema according to Swagger's specs. The result in the .json will be the same in '@schema'.
app.get('/path', (req, res) => {
...
/* #swagger.parameters['body'] = {
in: 'body',
'@schema': {
"required": ["name"],
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "string",
"minLength": 2,
"maxLength": 250,
"example": "Some example..."
}
}
}
} */
...
});
In the case above, the schema in the .json will be the same in '@schema'.
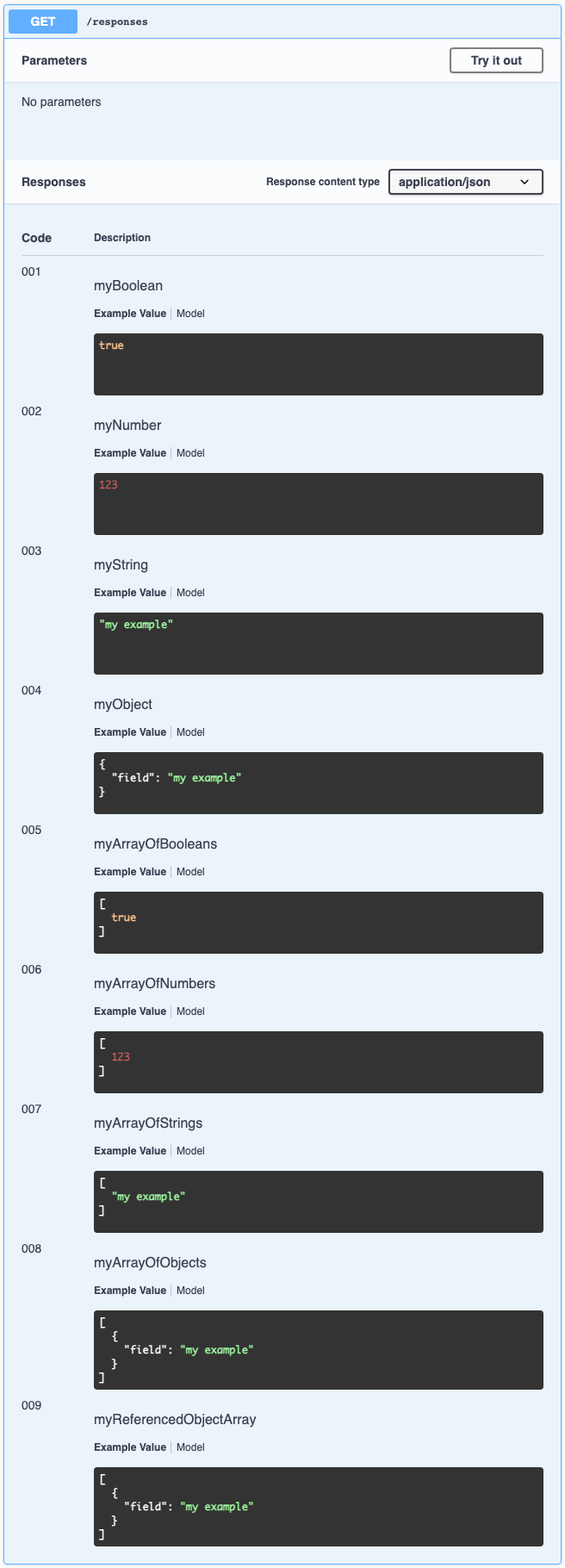
Example of Definitions
The following are some examples of definitions:
Definitions:
const doc = {
...
definitions: {
myBoolean: true,
myNumber: 123,
myString: 'my example',
myObject: {
field: 'my example'
},
myArrayOfBooleans: [true],
myArrayOfNumbers: [123],
myArrayOfStrings: ['my example'],
myArrayOfObjects: [
{
field: 'my example'
}
],
myReferencedObjectArray: [{ $ref: '#/definitions/myObject' }]
};
};
Endpoint:
app.get('/responses', (req, res) => {
/* #swagger.responses[001] = {
description: 'myBoolean',
schema: { $ref: '#/definitions/myBoolean' }
} */
/* #swagger.responses[002] = {
description: 'myNumber',
schema: { $ref: '#/definitions/myNumber' }
} */
/* #swagger.responses[003] = {
description: 'myString',
schema: { $ref: '#/definitions/myString' }
} */
/* #swagger.responses[004] = {
description: 'myObject',
schema: { $ref: '#/definitions/myObject' }
} */
/* #swagger.responses[005] = {
description: 'myArrayOfBooleans',
schema: { $ref: '#/definitions/myArrayOfBooleans' }
} */
/* #swagger.responses[006] = {
description: 'myArrayOfNumbers',
schema: { $ref: '#/definitions/myArrayOfNumbers' }
} */
/* #swagger.responses[007] = {
description: 'myArrayOfStrings',
schema: { $ref: '#/definitions/myArrayOfStrings' }
} */
/* #swagger.responses[008] = {
description: 'myArrayOfObjects',
schema: { $ref: '#/definitions/myArrayOfObjects' }
} */
/* #swagger.responses[009] = {
description: 'myReferencedObjectArray',
schema: { $ref: '#/definitions/myReferencedObjectArray' }
} */
});
The result will be: